The contents of each can be used to calculate different colcoalization results. You can see they are all close to zero, and in the results you can see that on average the randomized R value is about zero, meaning that the randomized images all had no correlation with the real image. The result of this tests tell us if the Pearsons r and split Manders' coefficients we measure are better than pure chance or not. This e-mail message and any attachments are confidential and proprietary to PerkinElmer, Inc. It does the Costes method auto threshold determination. They are listed here, in arguably order of usefulness: 
| Uploader: | Masida |
| Date Added: | 10 January 2015 |
| File Size: | 17.87 Mb |
| Operating Systems: | Windows NT/2000/XP/2003/2003/7/8/10 MacOS 10/X |
| Downloads: | 16118 |
| Price: | Free* [*Free Regsitration Required] |
The thresholded Mander's coefficients are probably the numbers you would publish not the Pearson's coefficients as these are less informative.
Colocalization Analysis
Free forum by Nabble. Maybe we can decide if the data is suitable for this analysis or not? We notice that the shades and hues of colours look different according to what other colours they are next to! Right now, the advantage that JaCoP plugin has is a prettier interface. Here we see if there is correlation immediately by eye, in the presence of a cloud of information in the middle of the 2D histogram. The Colocalization Threshold plugin performs several functions for you in one go.
This is plain wrong. Questions you should ask before attempting colocalisation analysis from 2 colour channel images, using the pixel intensity spatial correlation methods of Manders and Costes:. The methods of Pearson, Manders, Costes and Li should work very well for this sample, but maybe we can see some problems with the data?
It makes a linear regression fit of the data in the scatter plot. Let's open a sample data set that we know should have very good colocalization because the 2 subunits of a dimeric protein are stained with green and red dyes respectively.
You could also have a look on the wiki page on fiji. Just have a look at this image:.

None of this gives sensible results unless you imavej your imaging hardware set up appropriately and have acquired images properly, and have performed appropriate controls for bleed-through and chromatic shift etc. Which is a good thing!
ImageJ - Colocalization analysis using JACoP or Fiji
I am doing colocalization of proteins using confocal microscopy and turned initialially to the Colocalization plugin within ImageJ using the MacMaster University biophotonics distribution which is quite stale.
These are both good things for the quality of the result. I ended up helping debug the Coloc2 lmagej which was also not properly handling ROI's. First you have to define what you mean by colocalisation, and that is not trivial.
Colocalization Analysis - ImageJ
If the image is one big pixel, everything will colocalize! We can fit that cloud with a linear jmagej and measure correlation coefficients. The two circles look like different colours, but they are exactly the same if you measure the pixel values. Hello Aldo and Lenny I, too, would suggest one more try of Coloc 2. Thanks for your help. While the old plugins are described below as well, we recommend that you use Coloc 2 instead.
This test is performed by randomly scrambling the blocks of pixels instead of individual pixels, because each pixel's intensity is correlated with its neighboring pixels in one image, and then measuring the correlation of this image with the other unscrambled imaggej.
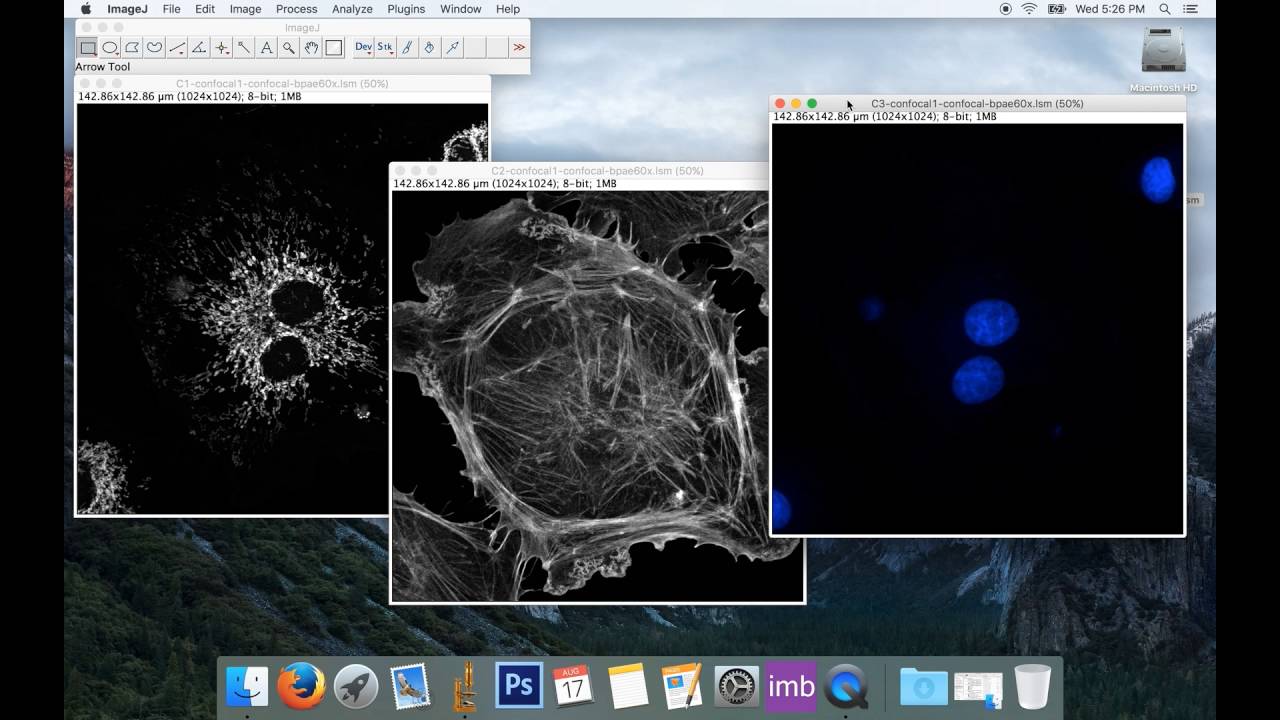
Is there a source for the Coloc 2 plugin for ImageJ? See here for hardware set up guidelines. To begin with, we should check the images for problems that might make the colocalisation analysis methods fail or be unreliable.
This page was last modified on 31 Julyat There is one coefficient per channel, which tells you the proportion of signal in that channels that colocalises with the other channel. Thanks everyone for the prompt response.
If not then we need to calibrate them so we know the spatial sampling rate think pixel or voxel size in x, y and z. We must colocalise at some defined and explicit spatial scale: On the other hand, if you are only interested in larger objects, and not the smallest iagej the objective can see, it makes sense to have larger pixels or voxels. This method uses an iterative procedure to determine what pair of thresholds for the 2 channels of the scatterplot give a Pearson's correlation coefficient r of zero for the pixels below the thresholds.

Комментарии
Отправить комментарий